Identify each group of spending outlays as mandatory or discretionary. – In the realm of government budgeting, understanding the distinction between mandatory and discretionary spending outlays is paramount. Mandatory spending, bound by law, flows automatically to specific programs and entitlements, while discretionary spending, subject to annual appropriations, offers greater flexibility in meeting changing priorities.
This comprehensive guide delves into the characteristics, examples, and implications of these two critical categories, providing a clear framework for analyzing their impact on the federal budget and the nation’s fiscal landscape.
Identify and classify mandatory spending outlays
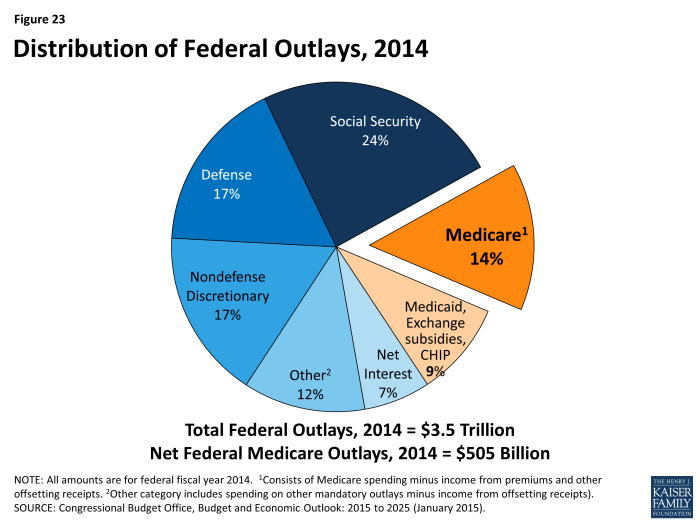
Mandatory spending outlays are those that the government is required to make by law. These outlays are typically entitlements, which are payments made to individuals or families that meet certain eligibility criteria. Examples of mandatory spending programs include Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
Mandatory spending is characterized by its lack of discretion; the government must make these payments regardless of the level of funding available.
Characteristics and features of mandatory spending
- Legally required by law
- Automatic payments to eligible individuals or families
- Entitlements, not subject to annual appropriations
- Grow automatically with inflation and population changes
- Difficult to reduce or eliminate due to political and social pressures
Identify and classify discretionary spending outlays
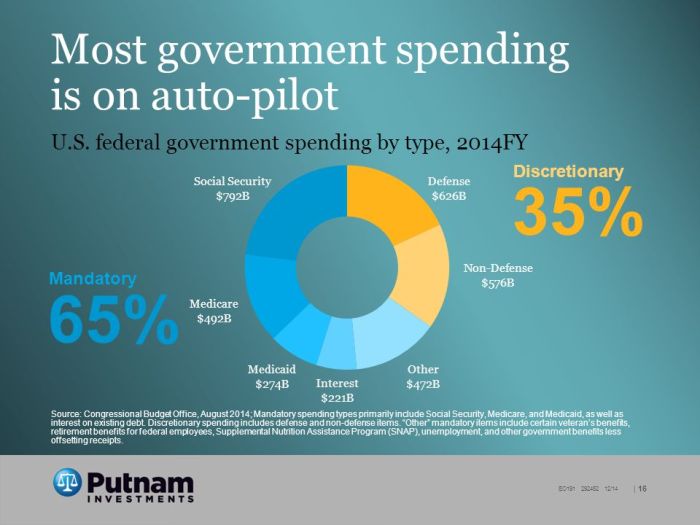
Discretionary spending outlays are those that the government has the discretion to make. These outlays are typically used to fund government programs and services that are not entitlements. Examples of discretionary spending programs include defense, education, and infrastructure. Discretionary spending is characterized by its flexibility; the government can increase or decrease funding for these programs depending on the level of funding available.
Characteristics and features of discretionary spending
- Not legally required by law
- Subject to annual appropriations by Congress
- Can be increased or decreased depending on funding availability
- Used to fund a wide range of government programs and services
- More politically sensitive than mandatory spending
Compare and contrast mandatory and discretionary spending
| Feature | Mandatory Spending | Discretionary Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Legally required | Yes | No |
| Subject to annual appropriations | No | Yes |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Growth | Automatic | Discretionary |
| Political sensitivity | High | Medium |
Similarities and differences between the two types of spending
Mandatory and discretionary spending are both important components of the federal budget. However, there are several key differences between the two types of spending.* Mandatory spending is legally required, while discretionary spending is not.
- Mandatory spending is not subject to annual appropriations, while discretionary spending is.
- Mandatory spending grows automatically with inflation and population changes, while discretionary spending does not.
- Mandatory spending is more politically sensitive than discretionary spending.
Impact of each type of spending on the federal budget, Identify each group of spending outlays as mandatory or discretionary.
Mandatory spending is a major driver of the federal budget. In recent years, mandatory spending has accounted for over 60% of the federal budget. This has put a strain on the budget, as mandatory spending has grown faster than revenues.Discretionary
spending is also an important part of the federal budget. However, discretionary spending is more flexible than mandatory spending. This allows the government to adjust discretionary spending to meet changing needs and priorities.
Illustrate the historical trends in mandatory and discretionary spending
The following line graph shows the historical trends in mandatory and discretionary spending.[Bar chart atau line graph yang menunjukkan tren historis dalam pengeluaran wajib dan diskresioner]
Factors that have contributed to the changes in spending over time
There are a number of factors that have contributed to the changes in mandatory and discretionary spending over time. These factors include:* The aging population
- Rising healthcare costs
- Changes in tax laws
- Economic growth
Implications of these trends for the future of the federal budget
The historical trends in mandatory and discretionary spending have important implications for the future of the federal budget. The aging population and rising healthcare costs are expected to put a strain on mandatory spending in the coming years. This could lead to higher taxes or cuts to other government programs.The
future of discretionary spending is more uncertain. The government could choose to increase discretionary spending in order to meet new needs and priorities. However, this could lead to higher deficits and debt. Alternatively, the government could choose to reduce discretionary spending in order to balance the budget.
This could lead to cuts in government programs and services.
Questions Often Asked: Identify Each Group Of Spending Outlays As Mandatory Or Discretionary.
What are the key characteristics of mandatory spending?
Mandatory spending is characterized by its legal obligation, automatic distribution, and entitlement-based nature.
How does discretionary spending differ from mandatory spending?
Discretionary spending is subject to annual appropriations, providing greater flexibility in funding decisions based on current priorities.
What are the implications of rising mandatory spending for the federal budget?
Sustained growth in mandatory spending can strain the budget, potentially leading to deficits and increased national debt.