At stp which substance has metallic bonding – Metallic bonding at standard temperature and pressure (STP) is a fascinating phenomenon that imparts distinct properties to certain substances. This type of bonding arises from the unique behavior of metal atoms, leading to the formation of a “sea of electrons” that holds the positively charged metal ions together.
Understanding the nature of metallic bonding at STP is crucial for comprehending the behavior and applications of various materials.
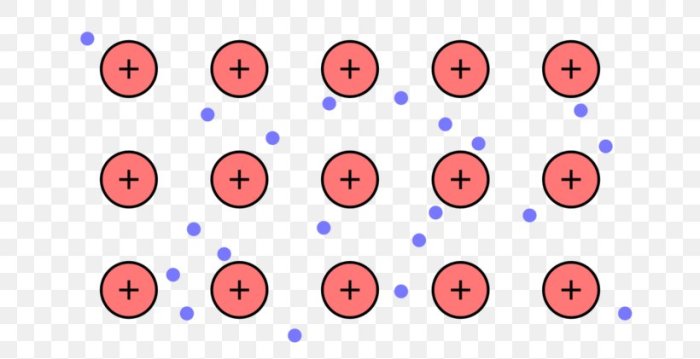
Metallic bonding occurs when metal atoms lose their outermost electrons, forming positively charged metal ions. These ions are then surrounded by a mobile cloud of delocalized electrons, which are free to move throughout the metal lattice. This arrangement results in a strong electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and the negative electron cloud, giving rise to the characteristic properties of metals.
Metallic Bonding at STP: At Stp Which Substance Has Metallic Bonding
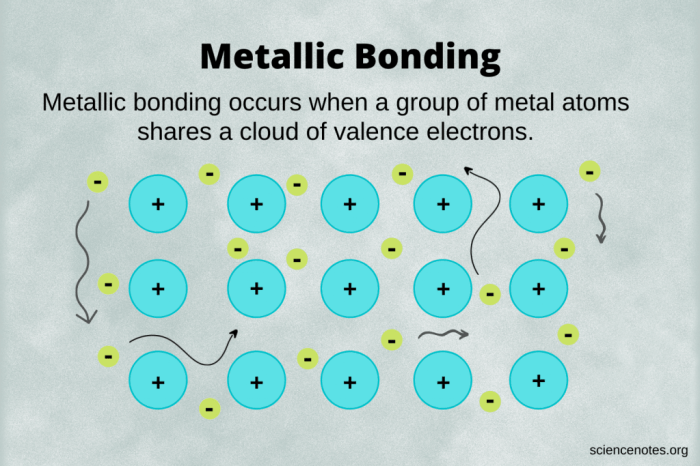
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that occurs between metal atoms. In metallic bonding, the metal atoms share their valence electrons in a sea of electrons that surrounds the positively charged metal ions. This sea of electrons holds the metal ions together and gives metals their characteristic properties, such as their high electrical and thermal conductivity.
Metallic bonding occurs at STP (standard temperature and pressure) in metals such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and aluminum. These metals have low ionization energies, which means that their valence electrons are easily removed. When these electrons are removed, the metal atoms become positively charged ions.
The positive ions are attracted to the sea of electrons, which holds them together and forms the metallic bond.
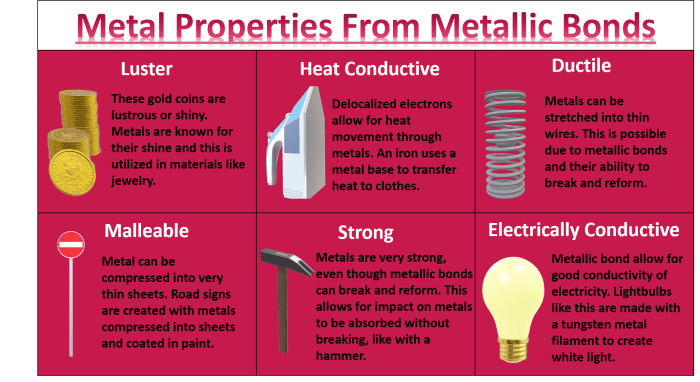
Properties of Metallic Bonding
Substances with metallic bonding have several characteristic physical properties. They are typically:
- Shiny
- Malleable
- Ductile
- Good conductors of heat and electricity
The shiny appearance of metals is due to the fact that they reflect light waves. The malleability and ductility of metals is due to the fact that the metal ions can move easily within the sea of electrons. The high electrical and thermal conductivity of metals is due to the fact that the valence electrons are free to move throughout the metal.
Substances with metallic bonding also have several characteristic chemical properties. They are typically:
- Reactive
- Form ionic compounds
The reactivity of metals is due to the fact that they have low ionization energies. This means that they can easily lose their valence electrons and form positive ions. The formation of ionic compounds occurs when metals react with non-metals.
In these reactions, the metal atoms lose their valence electrons to the non-metal atoms, forming positive ions and negative ions, respectively.
Comparison of Metallic Bonding to Other Bonding Types, At stp which substance has metallic bonding
Metallic bonding is different from ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and hydrogen bonding.
Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal. In ionic bonding, the metal atom loses one or more electrons to the non-metal atom, forming a positive ion and a negative ion, respectively. The positive and negative ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces.
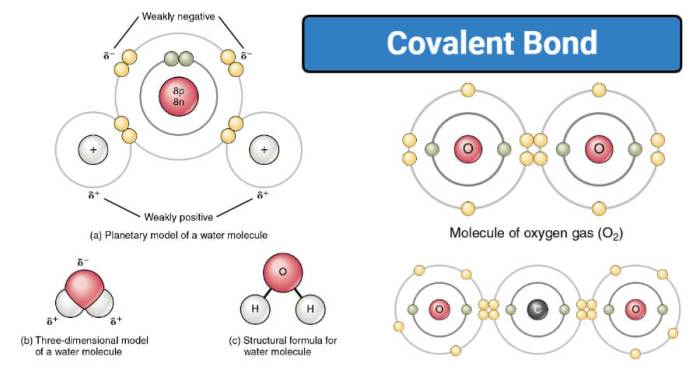
Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metal atoms. In covalent bonding, the two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons form a covalent bond between the two atoms.
Hydrogen bonding occurs between a hydrogen atom and a electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. In hydrogen bonding, the hydrogen atom forms a dipole with the electronegative atom. The dipole of the hydrogen atom is attracted to the dipole of the electronegative atom, forming a hydrogen bond.
Applications of Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is used in a wide variety of applications. Some of the most common applications include:
- Electrical wiring
- Plumbing
- Construction
- Transportation
Metallic bonding is also used in a variety of industrial applications, such as:
- Chemical processing
- Manufacturing
- Power generation
Metallic bonding is an important type of chemical bonding that is used in a wide variety of applications. The unique properties of metals, such as their high electrical and thermal conductivity, make them ideal for use in a variety of applications.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the defining characteristic of metallic bonding at STP?
Metallic bonding at STP is characterized by the formation of a “sea of electrons” that surrounds positively charged metal ions, resulting in a strong electrostatic attraction.
How does metallic bonding contribute to the electrical conductivity of metals?
The mobile cloud of delocalized electrons in metallic bonding allows for the easy flow of electric current, giving metals their high electrical conductivity.
What are some examples of substances that exhibit metallic bonding at STP?
Sodium, potassium, copper, aluminum, and iron are common examples of substances that exhibit metallic bonding at STP.