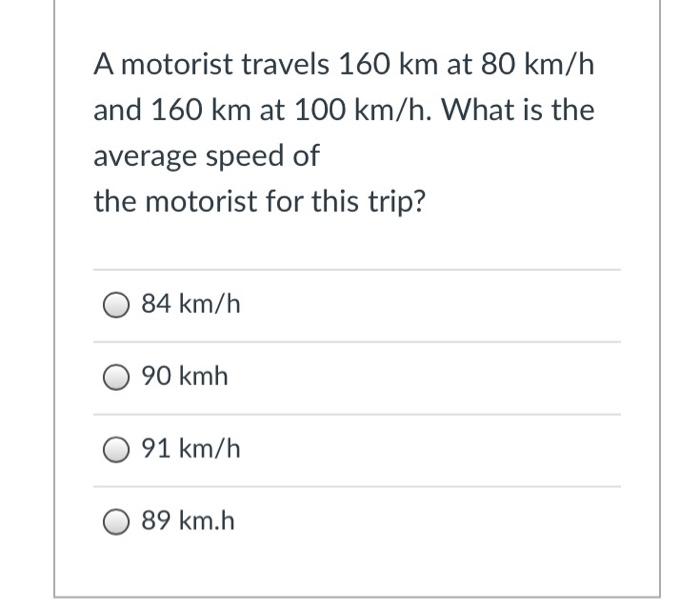
As a motorist travels 160 km at 80 takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with precision, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Embark on a journey where the relationship between speed, distance, and time unfolds, revealing the intricate tapestry that governs our everyday movements.
Delving into the heart of the matter, we will explore the equations that bind these three elements, unraveling the secrets of their interconnectedness. Real-world examples will illuminate the practical applications of these principles, demonstrating their relevance in countless aspects of our lives.
Speed and Distance

Speed and distance are two fundamental concepts in physics. Speed is the rate at which an object moves, while distance is the total length of the path traveled by the object. These two concepts are closely related, as the speed of an object determines the distance it can travel in a given amount of time.
The relationship between speed, distance, and time can be expressed mathematically using the following equation:
Speed = Distance / Time
This equation shows that the speed of an object is equal to the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance. For example, if an object travels 100 kilometers in 2 hours, its speed is 50 kilometers per hour.
The relationship between speed and distance is also evident in many real-world scenarios. For example, the speed of a car determines how far it can travel in a given amount of time. Similarly, the speed of a pedestrian determines how far they can walk in a given amount of time.
Time and Distance
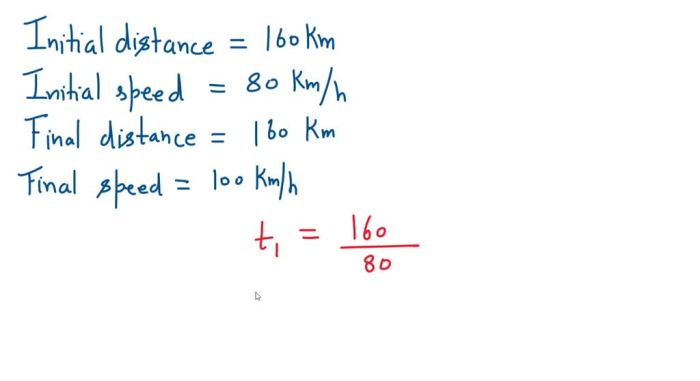
Time and distance are closely related in the realm of motion. The distance traveled by an object is directly proportional to the time taken to cover that distance, assuming a constant speed. This relationship can be mathematically expressed using the following equation:“`Distance = Speed × Time“`where:* Distance is measured in kilometers (km), miles (mi), or any other unit of length.
- Speed is measured in kilometers per hour (km/h), miles per hour (mph), or any other unit of speed.
- Time is measured in hours (h), minutes (min), or any other unit of time.
This equation implies that if the speed remains constant, doubling the time taken will result in doubling the distance covered, and vice versa.
Examples of Time and Distance in Real-World Scenarios
* A car traveling at a constant speed of 60 km/h will cover a distance of 120 km in 2 hours.
- A cyclist traveling at a constant speed of 15 mph will cover a distance of 30 miles in 2 hours.
- A pedestrian walking at a constant speed of 4 km/h will cover a distance of 8 km in 2 hours.
Understanding the relationship between time and distance is essential for planning journeys, estimating travel times, and calculating distances traveled.
A motorist who travels 160 km at 80 km/h would complete the journey in two hours. In the case of hoffman v. red owl stores inc , the plaintiff was awarded damages for injuries sustained in a car accident. The motorist in our example, traveling at the same speed, would have covered 160 km in the same time.
Speed, Distance, and Time Calculations

Speed, distance, and time are fundamental concepts in physics and everyday life. Understanding how to calculate these quantities is essential for various applications, such as planning trips, estimating travel times, and analyzing motion.
Speed, Distance, and Time Equations
The relationship between speed, distance, and time is expressed by the following equations:
- Speed = Distance / Time
- Distance = Speed – Time
- Time = Distance / Speed
How to Use the Equations
- To calculate speed:Divide the distance traveled by the time taken.
- To calculate distance:Multiply the speed by the time taken.
- To calculate time:Divide the distance traveled by the speed.
Examples
- A car travels 240 kilometers in 3 hours. What is its speed? Speed = 240 km / 3 h = 80 km/h
- A train travels at a speed of 120 km/h for 2 hours. What distance does it cover? Distance = 120 km/h – 2 h = 240 km
- A cyclist rides 15 kilometers in 45 minutes. How long did it take? Time = 15 km / 15 km/h = 1 h
Applications of Speed, Distance, and Time Calculations
Speed, distance, and time calculations are essential in various fields, enabling us to solve practical problems involving motion. These calculations find applications in:
Transportation
- Journey Planning:Calculating travel time and fuel consumption for road trips, flights, and train journeys.
- Logistics:Optimizing delivery routes and estimating arrival times for goods transportation.
- Traffic Management:Monitoring traffic flow, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing measures to improve traffic efficiency.
Engineering
- Automotive Design:Determining vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and braking distances.
- Civil Engineering:Designing roads, bridges, and railways with appropriate speed limits and safety features.
- Aerospace Engineering:Calculating aircraft speeds, trajectories, and fuel consumption for efficient flight operations.
Sports
- Performance Analysis:Measuring athletes’ speed, acceleration, and endurance in track and field events, cycling, and swimming.
- Race Planning:Determining optimal race strategies, pacing, and finishing times.
- Training Optimization:Calculating training distances, speeds, and recovery times for improved performance.
Science and Research
- Physics:Studying motion, velocity, and acceleration in scientific experiments and demonstrations.
- Astronomy:Calculating the speed and distance of celestial objects, such as planets, stars, and galaxies.
- Medical Research:Measuring blood flow rates, heart rates, and other physiological parameters involving speed and time.
Factors Affecting Speed, Distance, and Time: A Motorist Travels 160 Km At 80
Speed, distance, and time are interdependent variables in motion. Several factors can affect the calculations involving these variables. Understanding these factors is crucial for making accurate calculations.
Factors affecting speed, distance, and time include:
Road Conditions
- Surface Type:Different road surfaces, such as asphalt, concrete, gravel, or dirt, affect vehicle speed.
- Road Geometry:Curves, slopes, and intersections influence speed and distance traveled.
- Traffic Conditions:Congestion, accidents, or road closures can significantly impact travel time.
Vehicle Characteristics
- Vehicle Type:Cars, trucks, and motorcycles have different speed capabilities.
- Engine Power:More powerful engines allow for higher speeds.
- Aerodynamics:Vehicle shape and design affect air resistance, influencing speed.
Driver Behavior
- Speed Limit:Legal speed limits must be considered.
- Driving Habits:Aggressive or cautious driving styles can affect speed and time.
- Reaction Time:Driver response time to unexpected events influences safety and travel time.
Environmental Conditions
- Weather:Rain, snow, or fog can reduce visibility and affect speed.
- Wind:Headwinds or tailwinds can influence vehicle speed.
- Altitude:Higher altitudes affect engine performance and speed.
Distance Measurement
- Accuracy of Measuring Equipment:Odometers or GPS devices may have varying levels of accuracy.
- Path Length:The actual distance traveled may differ from the straight-line distance.
To account for these factors, consider the following:
- Use reliable and accurate measuring equipment.
- Allow for additional time or distance when planning trips.
- Adjust speed based on road conditions and traffic.
- Be aware of environmental factors and their potential impact.
Advanced Applications of Speed, Distance, and Time Calculations

Speed, distance, and time calculations are not just limited to basic scenarios. They find extensive applications in advanced fields like physics and engineering, where complex systems demand precise calculations. Accuracy and precision are crucial in these applications, as even minor errors can lead to significant consequences.
In Physics, A motorist travels 160 km at 80
In physics, speed, distance, and time calculations are used to analyze motion and forces. For example, in projectile motion, the trajectory of an object is determined by calculating its initial velocity, launch angle, and the acceleration due to gravity. These calculations help physicists understand the motion of objects under various conditions.
In Engineering
In engineering, speed, distance, and time calculations are used in various disciplines, such as mechanical engineering, civil engineering, and aerospace engineering. For instance, in mechanical engineering, these calculations are used to design engines and transmissions that optimize performance and fuel efficiency.
In civil engineering, they are used to calculate the load-bearing capacity of bridges and buildings, ensuring structural integrity.
Importance of Accuracy and Precision
In advanced applications, accuracy and precision are of utmost importance. Inaccurate calculations can lead to incorrect predictions, faulty designs, and even safety hazards. For example, in aerospace engineering, precise calculations are essential for determining the trajectory of a spacecraft, ensuring it reaches its intended destination safely.
Essential FAQs
What is the formula for calculating speed?
Speed = Distance / Time
How do I calculate the time it takes to travel a certain distance?
Time = Distance / Speed
What factors can affect the accuracy of speed, distance, and time calculations?
Factors such as wind resistance, traffic conditions, and the accuracy of measuring instruments can influence the precision of these calculations.