Given ABCD is a trapezoid, a captivating exploration into the realm of quadrilaterals. A trapezoid, with its distinct shape and characteristics, holds a special place in the world of geometry, and its properties and applications extend far beyond the classroom.
As we delve into the intricacies of trapezoids, we will uncover their defining features, delve into their various types, and explore the practical applications that make them indispensable in fields as diverse as architecture, engineering, and design. Join us on this journey of discovery as we unravel the secrets of given ABCD is a trapezoid.
Definition of a Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral, a two-dimensional figure with four straight sides and four angles, having one pair of parallel sides.
Given ABCD is a trapezoid, we can apply various geometric principles to analyze its properties. For instance, if we know that RX = 4 and XS = 9, we can determine the value of XT using the relationship between the lengths of the parallel sides and the non-parallel sides of a trapezoid, as explained in this insightful article: if rx 4 and xs 9 then xt . Returning to our trapezoid ABCD, this knowledge helps us further understand its geometric characteristics and explore other related concepts.
In other words, a trapezoid is a polygon with four sides, where two sides are parallel and the other two sides are not parallel. The parallel sides are called bases, and the non-parallel sides are called legs.
Key Characteristics
- Has four sides and four angles
- Has one pair of parallel sides (bases)
- Has two non-parallel sides (legs)
- The angles opposite the parallel sides are supplementary (add up to 180 degrees)
Here is a visual representation of a trapezoid, with its sides and angles labeled:

Properties of a Trapezoid
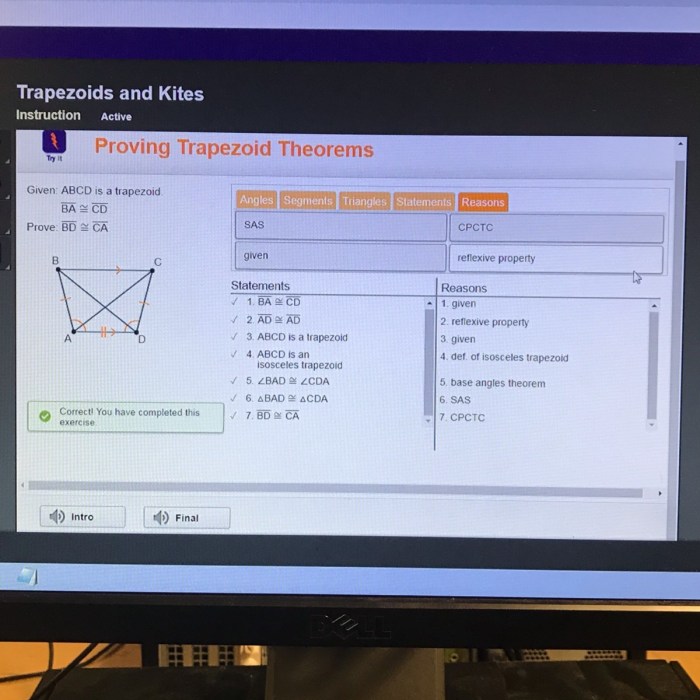
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides called bases. The other two sides, which are not parallel, are called legs. Trapezoids have several unique properties that distinguish them from other quadrilaterals.
Base and Leg Relationships
The bases of a trapezoid are always parallel, and their lengths can be different. The legs of a trapezoid are not parallel, and they can also have different lengths. The relationship between the bases and legs of a trapezoid is important in determining its shape and area.
- Base Angles:The angles formed by the bases and legs of a trapezoid are called base angles. The base angles are always supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees.
- Leg Angles:The angles formed by the legs and bases of a trapezoid are called leg angles. The leg angles are not necessarily supplementary, and they can vary in size.
- Diagonals:The diagonals of a trapezoid are the line segments that connect the opposite vertices. The diagonals of a trapezoid are not necessarily congruent, and they can intersect at any point inside the trapezoid.
Types of Trapezoids: Given Abcd Is A Trapezoid
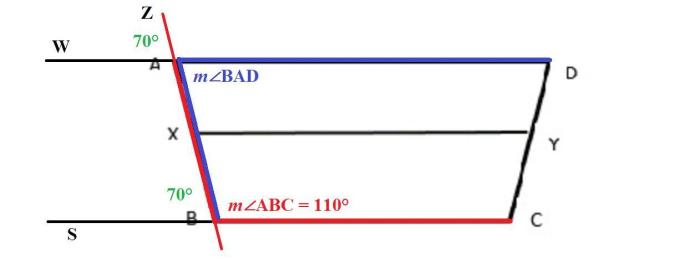
Trapezoids can be classified into different types based on their specific characteristics. The most common types are isosceles trapezoids, right trapezoids, and scalene trapezoids.
Isosceles Trapezoids
Isosceles trapezoids have two congruent sides and two congruent base angles. The congruent sides are the non-parallel sides, and the congruent base angles are the angles opposite the congruent sides. Isosceles trapezoids have the following properties:
- The diagonals are congruent.
- The base angles are supplementary.
- The area is given by the formula: A = (1/2) – (b1 + b2) – h, where b1 and b2 are the lengths of the bases and h is the height.
Right Trapezoids
Right trapezoids have one right angle. The right angle is usually formed by one of the bases and one of the non-parallel sides. Right trapezoids have the following properties:
- The diagonals are perpendicular.
- The area is given by the formula: A = (1/2) – b – h, where b is the length of the base and h is the height.
Scalene Trapezoids, Given abcd is a trapezoid
Scalene trapezoids have no congruent sides or congruent base angles. They are the most general type of trapezoid. Scalene trapezoids have the following properties:
- The diagonals are not congruent.
- The base angles are not supplementary.
- The area is given by the formula: A = (1/2) – (b1 + b2) – h, where b1 and b2 are the lengths of the bases and h is the height.
Geometric Formulas for Trapezoids
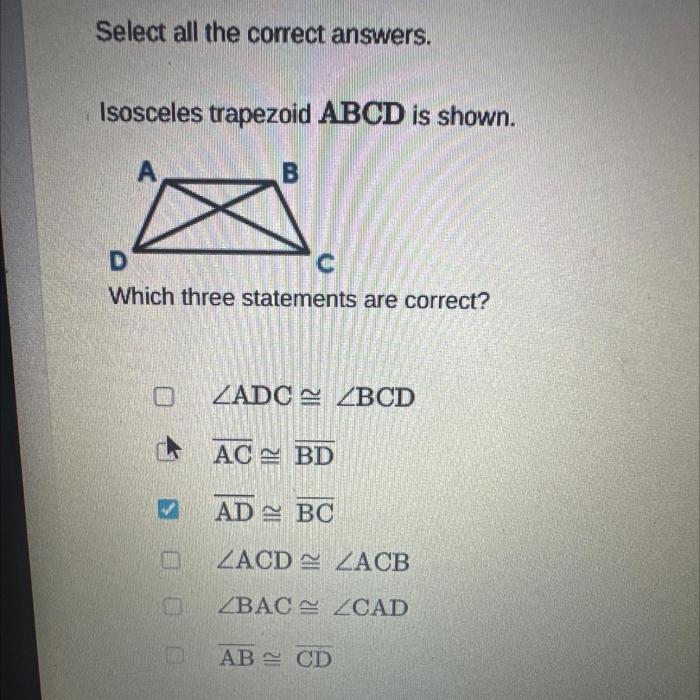
Trapezoids are quadrilaterals with two parallel sides. These formulas are essential for solving problems involving the area, perimeter, and height of a trapezoid.
Area of a Trapezoid
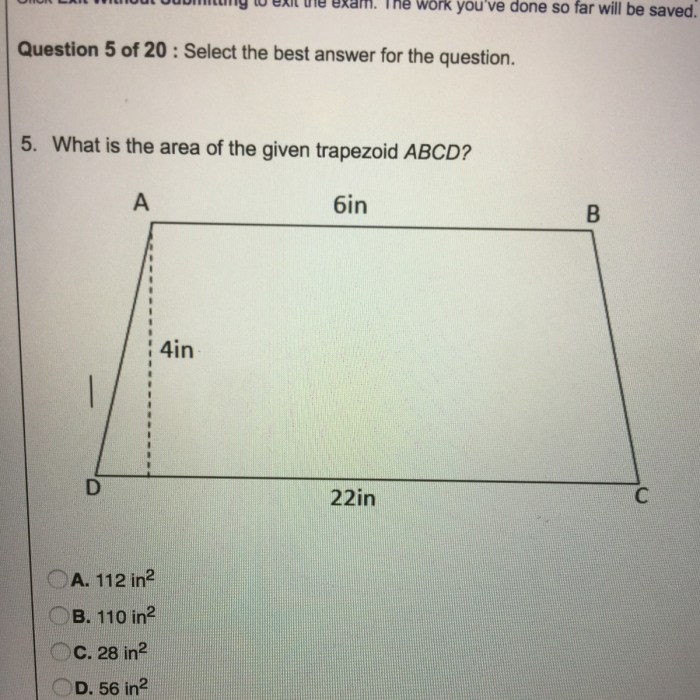
The area of a trapezoid is given by the formula:“`Area = (1/2)
- (Base1 + Base2)
- Height
“`where Base1 and Base2 are the lengths of the parallel sides, and Height is the distance between the parallel sides.For example, if a trapezoid has parallel sides of length 6 cm and 8 cm, and a height of 4 cm, then its area is:“`Area = (1/2)
- (6 cm + 8 cm)
- 4 cm = 28 cm²
“`
Perimeter of a Trapezoid
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. The formula for the perimeter is:“`Perimeter = Base1 + Base2 + Leg1 + Leg2“`where Base1 and Base2 are the lengths of the parallel sides, and Leg1 and Leg2 are the lengths of the non-parallel sides.For
example, if a trapezoid has parallel sides of length 6 cm and 8 cm, and non-parallel sides of length 5 cm and 7 cm, then its perimeter is:“`Perimeter = 6 cm + 8 cm + 5 cm + 7 cm = 26 cm“`
Height of a Trapezoid
The height of a trapezoid is the distance between the parallel sides. The formula for the height is:“`Height = (Area
2) / (Base1 + Base2)
“`where Area is the area of the trapezoid, and Base1 and Base2 are the lengths of the parallel sides.For example, if a trapezoid has an area of 28 cm² and parallel sides of length 6 cm and 8 cm, then its height is:“`Height = (28 cm²
2) / (6 cm + 8 cm) = 4 cm
“`
Real-World Applications of Trapezoids
Trapezoids, with their distinctive shape, find practical applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. Their unique geometry makes them suitable for specific functional roles in structures and objects.
In Architecture
- Roofs:Trapezoidal roofs are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. Their sloped sides provide drainage and can accommodate skylights or solar panels.
- Windows and Doors:Trapezoidal windows and doors add architectural interest and can provide natural light in spaces with limited wall space.
- Arches:Trapezoidal arches are found in bridges and other structures, providing support and aesthetic appeal.
In Engineering
- Bridges:Trapezoidal bridges are often used for pedestrian crossings or small spans, providing stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Machines:Trapezoidal components are found in machines, such as conveyor belts and pulleys, due to their ability to transfer forces efficiently.
- Automotive:Trapezoidal shapes are used in car hoods and trunks, contributing to aerodynamics and space utilization.
In Design
- Logos and Symbols:Trapezoids are incorporated into logos and symbols to create visual interest and convey specific meanings.
- Furniture:Trapezoidal tables and chairs provide stability and a unique aesthetic.
- Textiles:Trapezoidal patterns are used in fabrics and wallpaper, adding visual texture and interest.
FAQ Resource
What is the definition of a trapezoid?
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides, known as the bases, and two non-parallel sides, known as the legs.
What are the different types of trapezoids?
Trapezoids can be classified into three main types: isosceles trapezoids, right trapezoids, and scalene trapezoids, based on the lengths of their sides and the angles between them.
How do I calculate the area of a trapezoid?
The area of a trapezoid can be calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) x (sum of the lengths of the bases) x (height).